DRAFT_North Fork Stanislaus River Hydroelectric Project P-2409
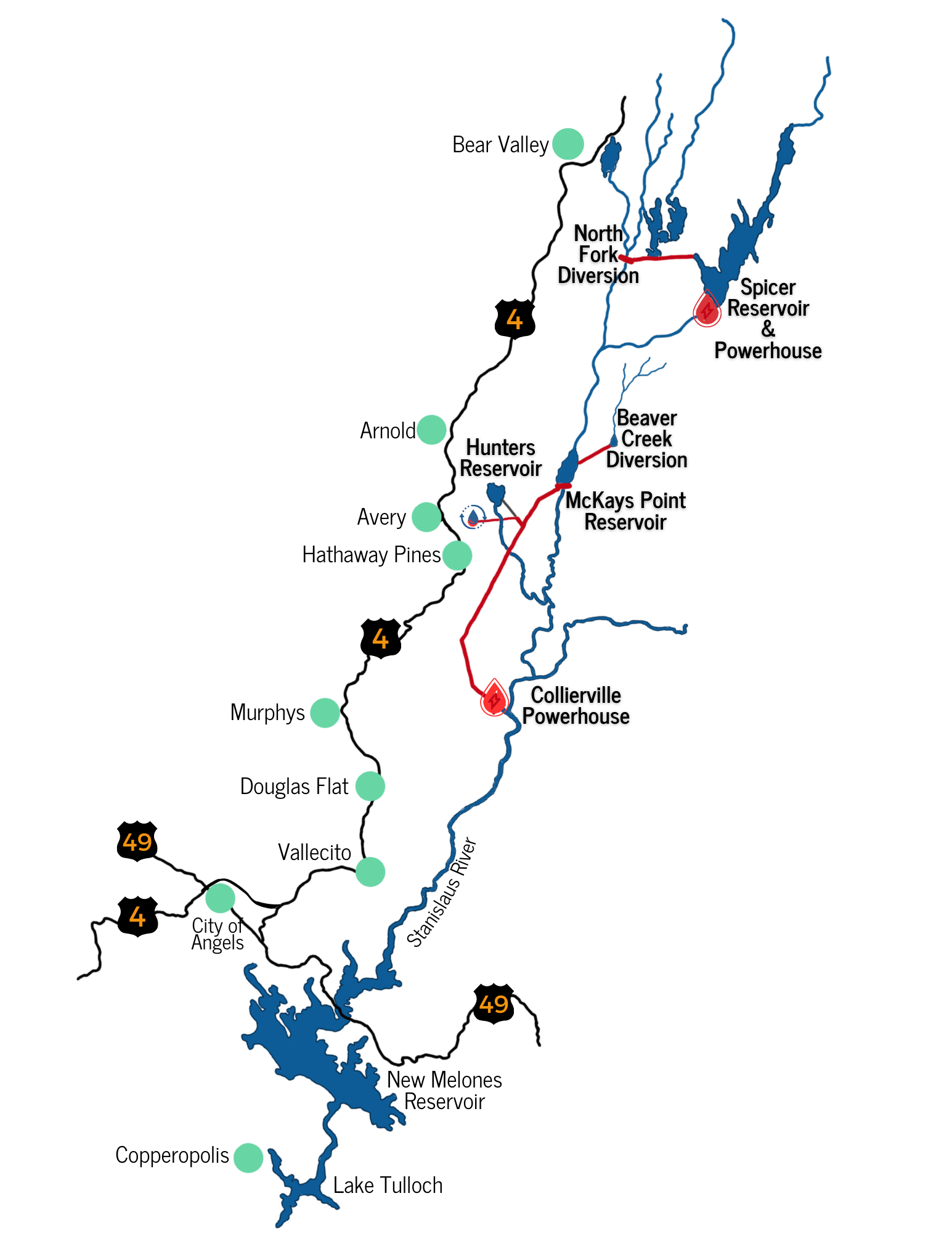
The North Fork Stanislaus River Hydroelectric Project (P-2409) combines water usage and electric power. This project encompasses 13 miles of tunnels, four dams, and two powerhouses. Located in the Sierra Nevada, the project travels along steep terrain, beginning at an elevation of 6,700 feet, while ultimately ending at the Collierville Power Plant at 1,099 feet.
Project Location
The Project is situated on the western slope of the Sierra Nevada, within the North Fork Stanislaus River (NFSR) Basin, spanning Calaveras, Tuolumne, and Alpine counties in California. Portions of the Project are located on federal lands managed by various agencies, including:
- The U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, as part of the Stanislaus National Forest (SNF);
- The U.S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Land Management (BLM), within the Sierra Resource Management Area; and
- The U.S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Reclamation (BOR), as part of the New Melones Reservoir Area.
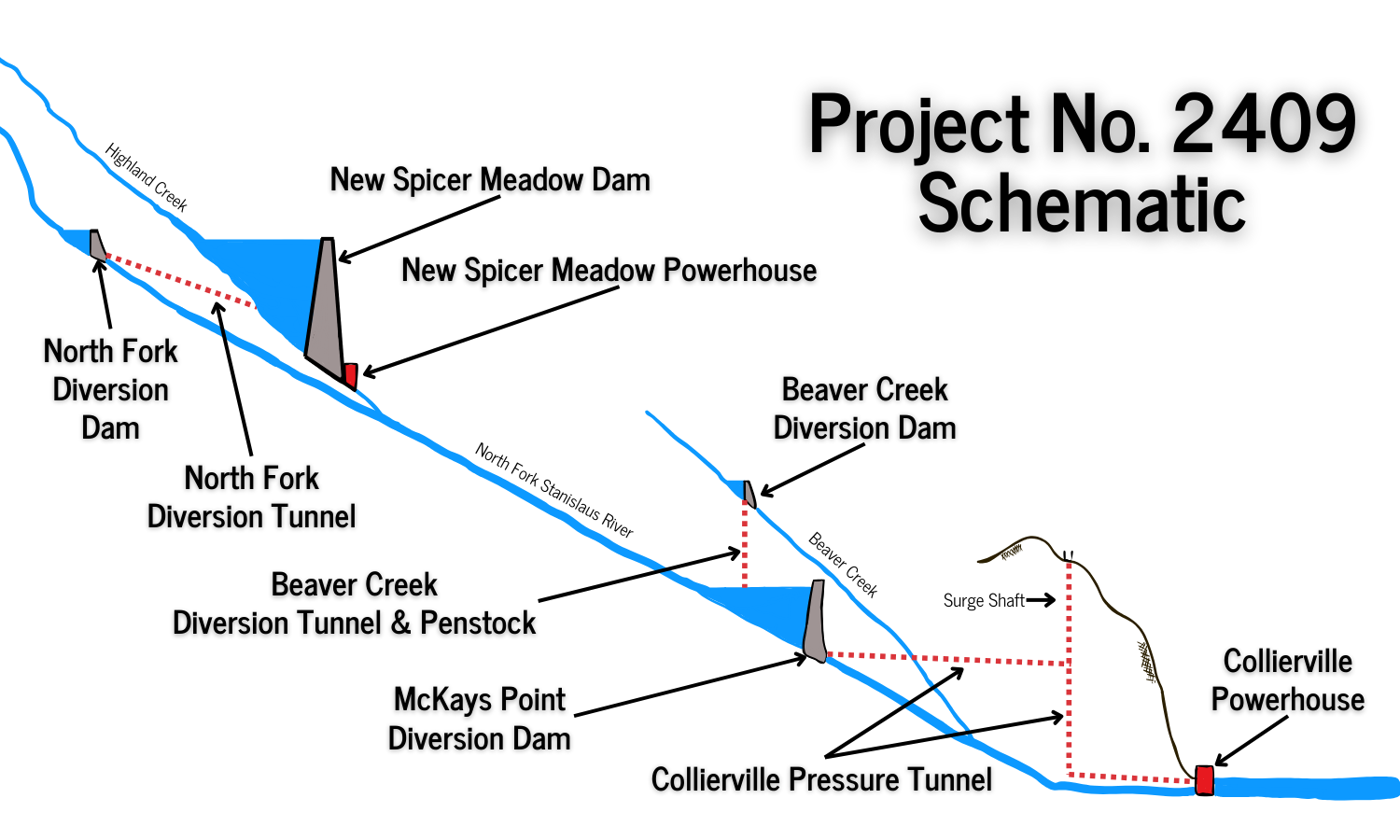
The project includes:
- North Fork Diversion Dam impoundment on the NFSR, formed by the North Fork Diversion Dam.
- North Fork Diversion Tunnel and outlet channel, which diverts water from the North Fork Diversion Dam to New Spicer Meadow Reservoir.
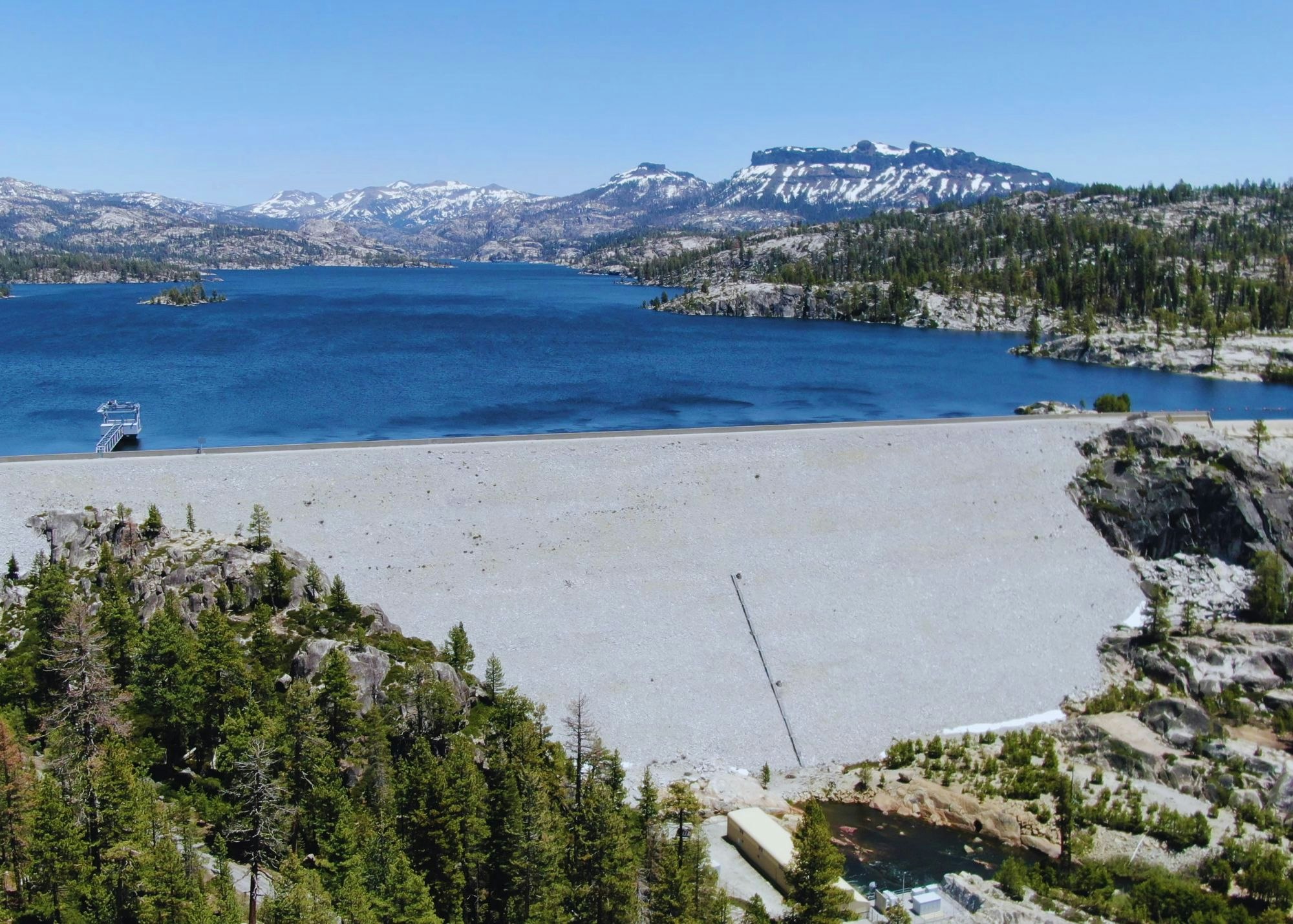
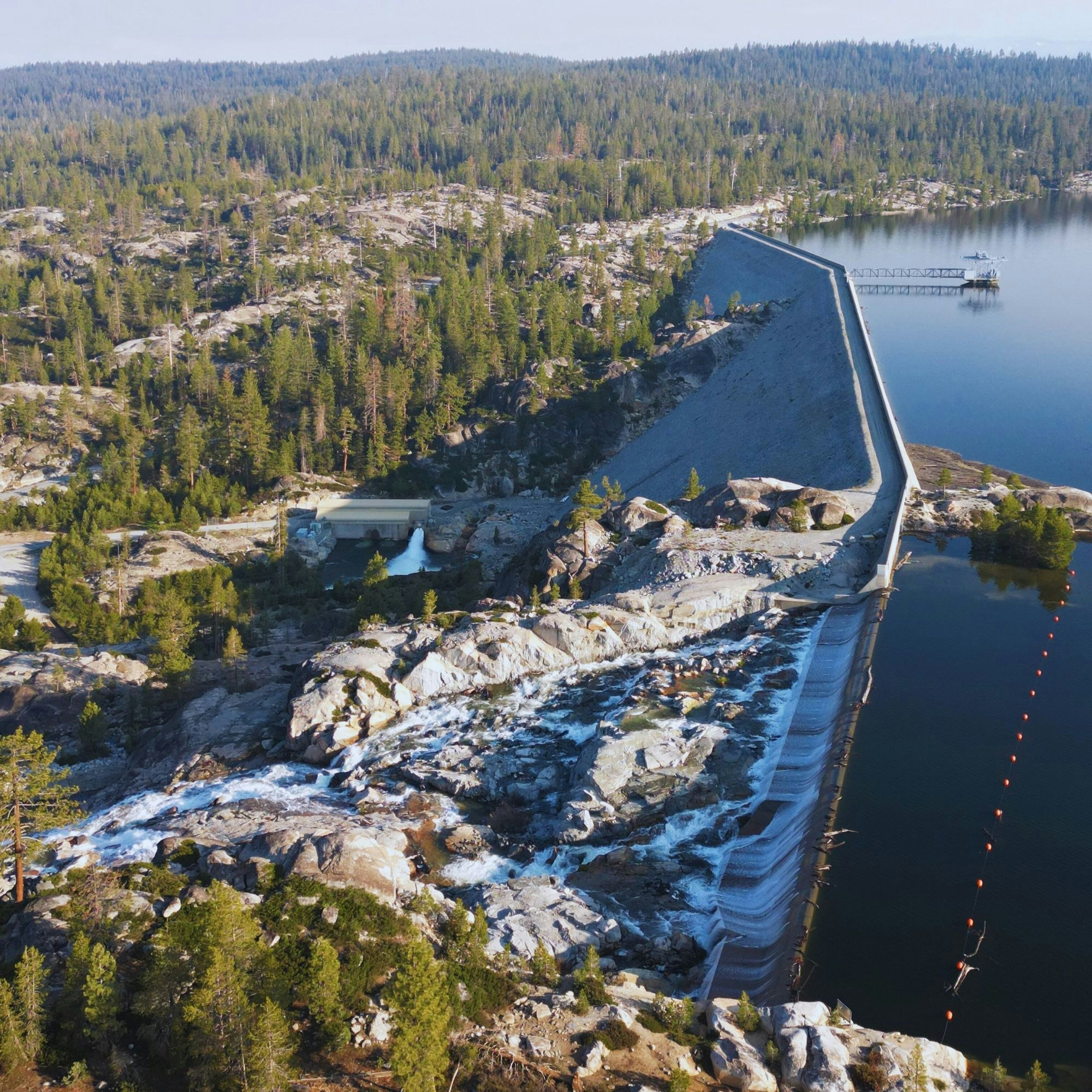
- New Spicer Meadow Reservoir on Highland Creek, a tributary to the NFSR, formed by New Spicer Meadow Dam.
- New Spicer Meadows Intake, containing three multi-level gates to deliver water to the New Spicer Meadow Powerhouse.
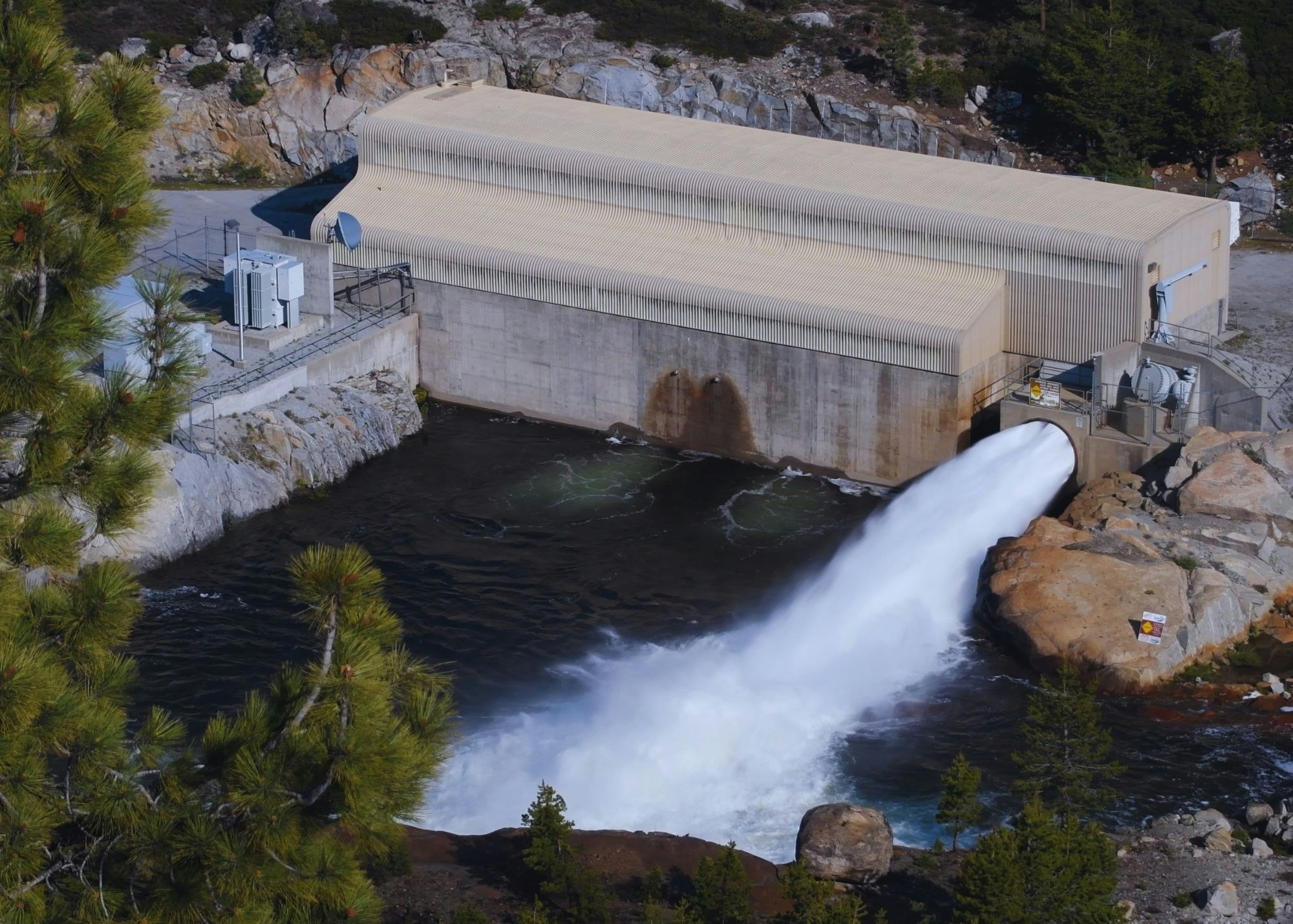
- New Spicer Meadow Powerhouse, located at the outlet works of the dam, includes three turbines with a total generating capacity of 5.7 megawatts (MW).
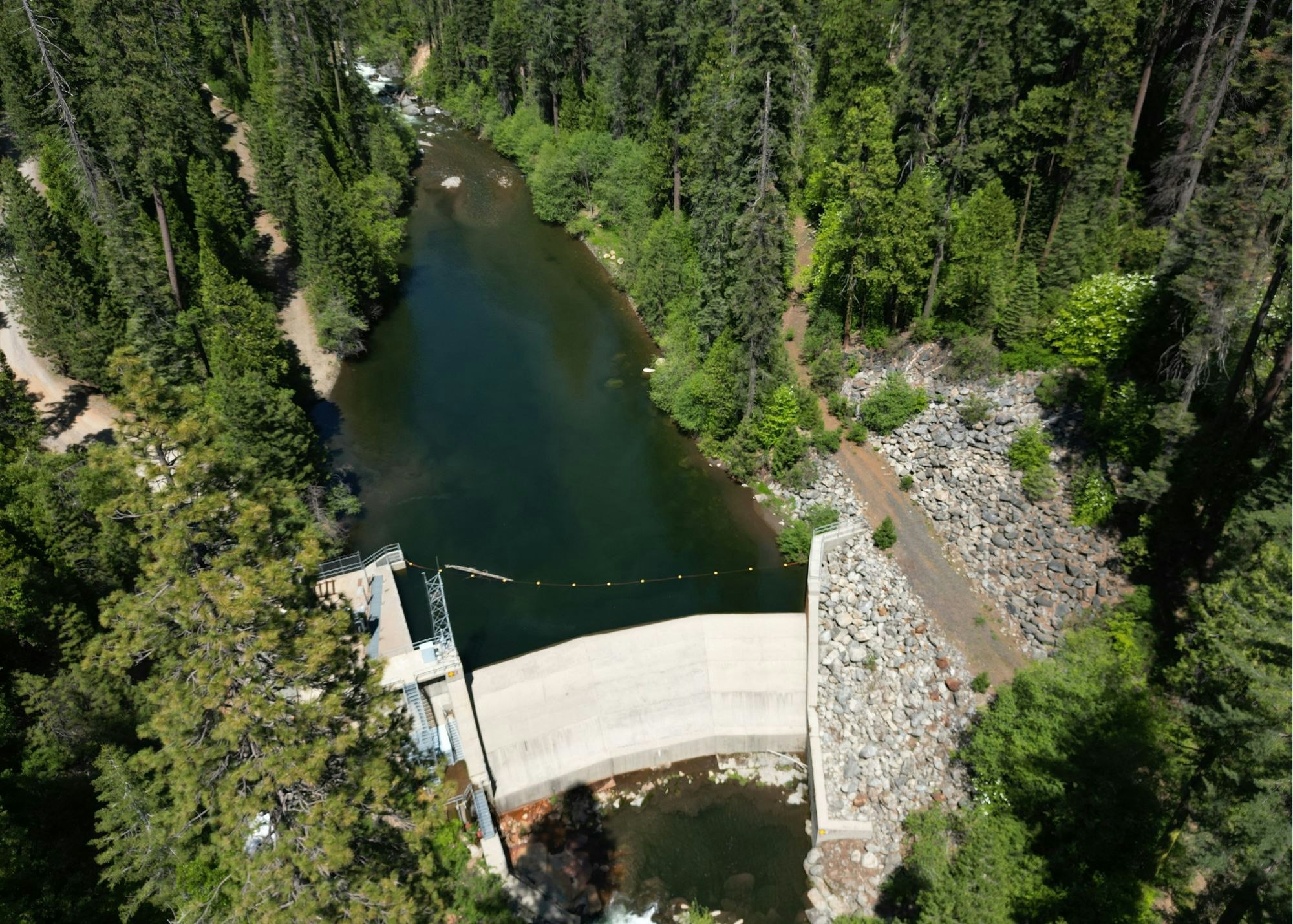
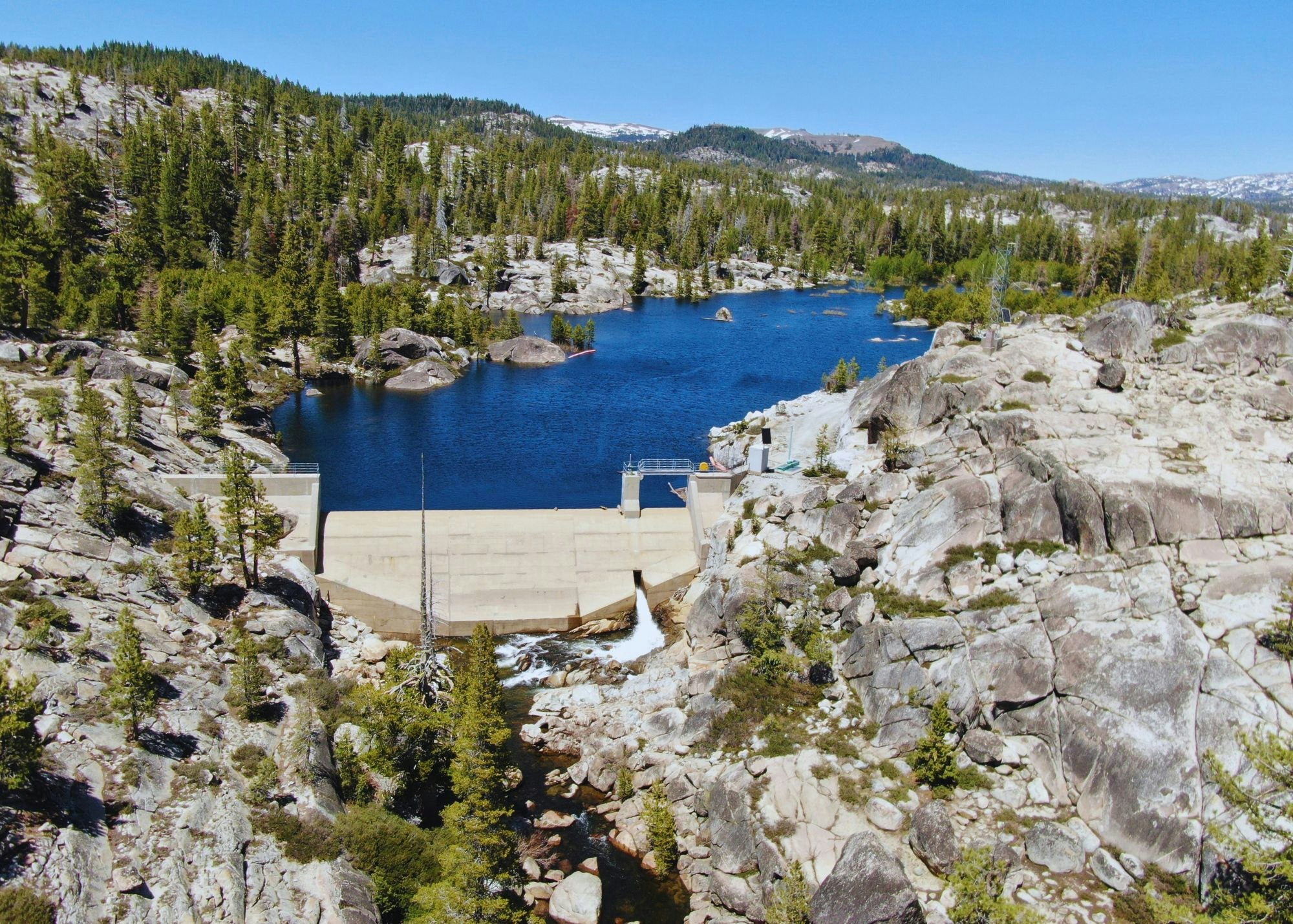
- Beaver Creek Diversion Dam impoundment on Beaver Creek, a tributary to the NFSR, formed by the Beaver Creek Diversion Dam.
- Beaver Creek Diversion Tunnel and Penstock, which diverts water from the Beaver Creek Diversion Dam to McKays Point Reservoir.
- McKays Point Reservoir on the NFSR, formed by McKays Point Diversion Dam.
- Collierville Intake and Tunnel, which diverts water from the McKays Point Diversion Dam to the Collierville Powerhouse.
- McKays Point Microturbine, located at the base of McKays Point Dam, includes a 200 kilowatt (kW) microturbine.
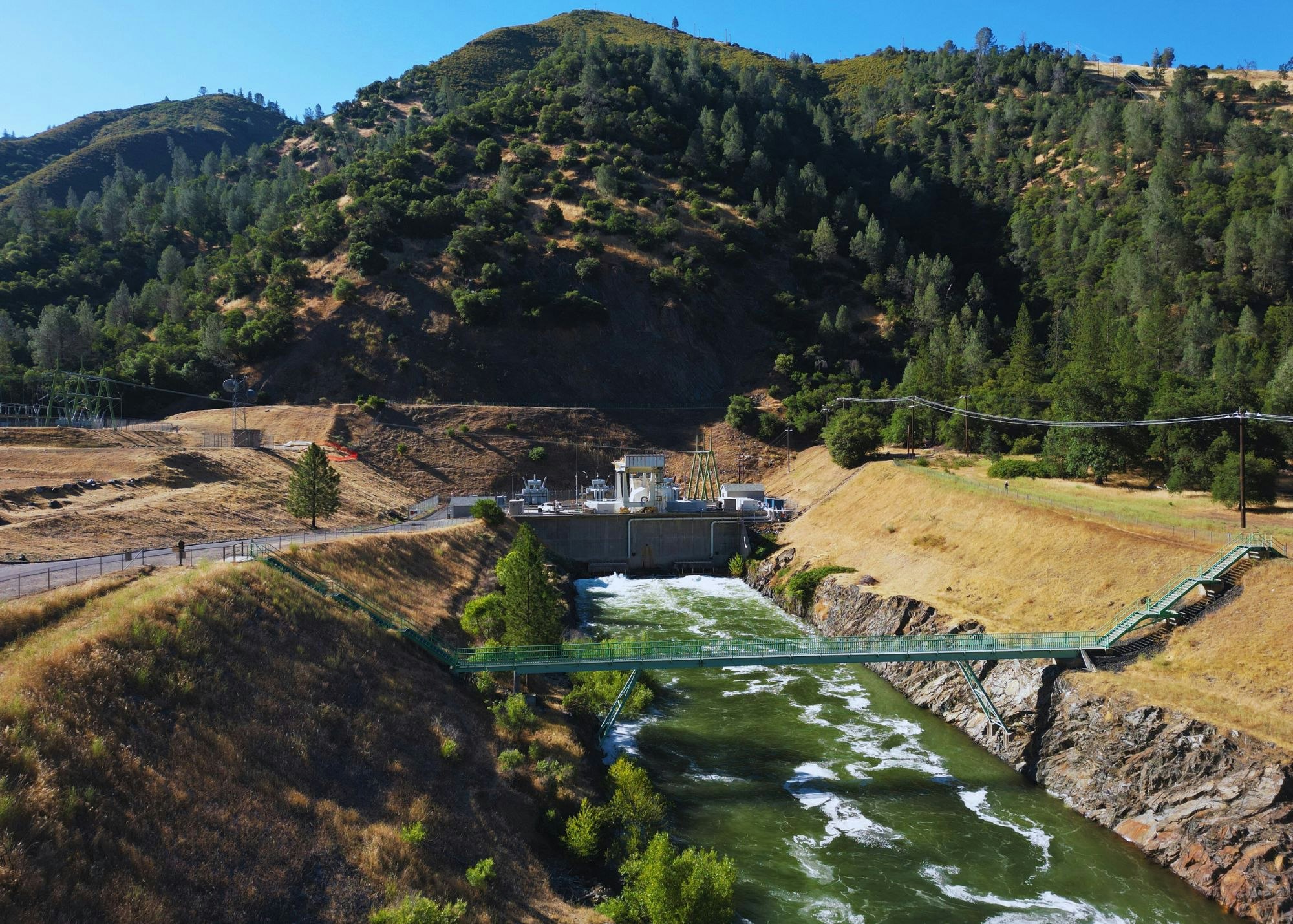
- Collierville Powerhouse, located on the Stanislaus River, with two equal-sized turbine-generator units with a total rated capacity of 256.8 MW.
- Collierville Tailrace, which delivers water from the Collierville Powerhouse to the Stanislaus River immediately upstream of BOR’s New Melones Reservoir.
- New Spicer Meadow Campground and New Spicer Meadow Boat Launch and Day Use Area.
Power from the project is transmitted by Northern California Power Agency’s Collierville and Spicer Meadow Transmission Line Project, FERC Project No. 11197.
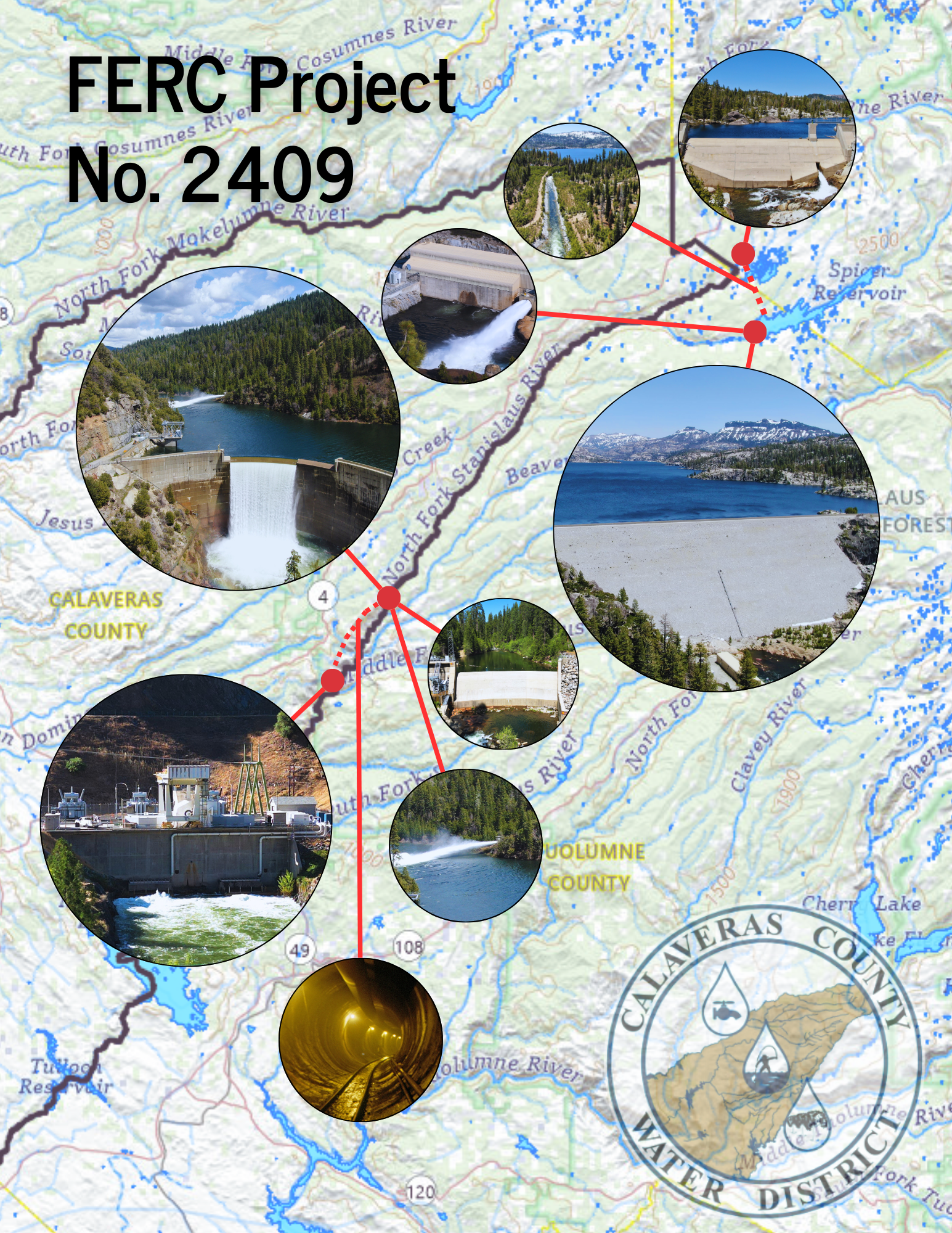
Melting snow, and Spring runoff collects in the New Spicer Meadow Reservoir. Additional water from the North Fork Stanislaus River is diverted to the reservoir through the two-mile North Fork Diversion Tunnel. Water is released from New Spicer Meadow Reservoir to meet recreational needs, fish flow, domestic and irrigation water usage. This water flows through Highland Creek, which meets the North Fork Stanislaus River. With the additional water from the Beaver Creek Diversion, the North Fork Stanislaus is finally impounded at McKays Point Reservoir where it enters an 8-mile tunnel to generate power at the Collierville Powerhouse.




.jpg?ixlib=rb-1.1.0&w=2000&h=2000&fit=max&or=0&s=600f3dd40990b306acda8b7f9606be80)


.jpg?ixlib=rb-1.1.0&w=2000&h=2000&fit=max&or=0&s=c4f94a6c19f52a1305cec9ea55de1328)





.jpg?ixlib=rb-1.1.0&w=2000&h=2000&fit=max&or=0&s=600f3dd40990b306acda8b7f9606be80)


.jpg?ixlib=rb-1.1.0&w=2000&h=2000&fit=max&or=0&s=c4f94a6c19f52a1305cec9ea55de1328)


.png?ixlib=rb-1.1.0&or=0&w=720&h=720&fit=max&auto=format%2Ccompress&s=358268bcca620907d1451152ce93461f)